最强最全面的Hive SQL开发指南,四万字全面解析
园陌本文整体分为两部分,第一部分是简写,如果能看懂会用,就直接从此部分查,方便快捷,如果不是很理解此SQl的用法,则查看第二部分,是详细说明,当然第二部分语句也会更全一些!
第一部分:
hive模糊搜索表:show tables like '*name*';
查看表结构信息:desc table_name;
查看分区信息:show partitions table_name;
加载本地文件:load data local inpath '/xxx/test.txt' overwrite into table dm.table_name;
从查询语句给table插入数据:insert overwrite table table_name partition(dt) select * from table_name;
导出数据到本地系统:insert overwrite local directory '/tmp/text' select a.* from table_name a order by 1;
创建表时指定的一些属性:
字段分隔符:row format delimited fields terminated by ' '
行分隔符:row format delimited lines terminated by ''
文件格式为文本型存储:stored as textfile
命令行操作:hive -e 'select table_cloum from table'执行一个查询,在终端上显示mapreduce的进度,执行完毕后,最后把查询结果输出到终端上,接着hive进程退出,不会进入交互模式
hive -S -e 'select table_cloum from table' -S,终端上的输出不会有mapreduce的进度,执行完毕,只会把查询结果输出到终端上。
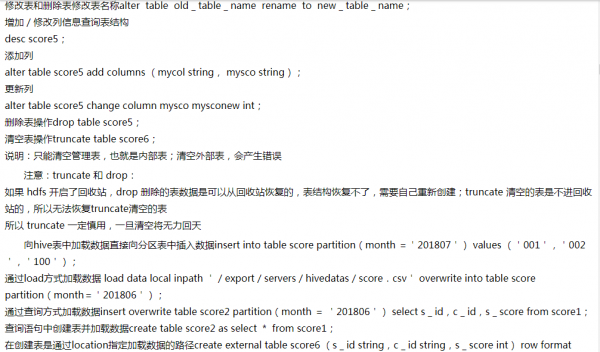
hive修改表名:alter table old_table_name rename to new_table_name;
hive复制表结构:create table new_table_name like table_name;
hive添加字段:alter table table_name add columns(columns_values bigint comment 'comm_text');
hive修改字段:alter table table_name change old_column new_column string comment 'comm_text';
删除分区:alter table table_name drop partition(dt='2021-11-30');
添加分区:alter table table_name add partition (dt='2021-11-30');
删除空数据库:drop database myhive2;
强制删除数据库:drop database myhive2 cascade;
删除表:drop table score5;
清空表:truncate table score6;
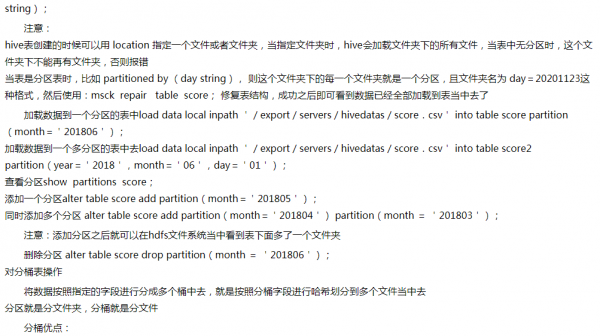
向hive表中加载数据
直接向分区表中插入数据:insert into table score partition(month ='202107') values ('001','002','100');通过load方式加载数据:load data local inpath '/export/servers/hivedatas/score.csv' overwrite into table score partition(month='201806');通过查询方式加载数据:insert overwrite table score2 partition(month = '202106') select s_id,c_id,s_score from score1;查询语句中创建表并加载数据:create table score2 as select * from score1;在创建表是通过location指定加载数据的路径:create external table score6 (s_id string,c_id string,s_score int) row format delimited fields terminated by ',' location '/myscore';export导出与import 导入 hive表数据(内部表操作):
create table techer2 like techer; --依据已有表结构创建表
export table techer to '/export/techer';
import table techer2 from '/export/techer';
20. hive表中数据导出
insert导出
将查询的结果导出到本地:insert overwrite local directory '/export/servers/exporthive' select * from score;
将查询的结果格式化导出到本地:insert overwrite local directory '/export/servers/exporthive' row format delimited fields terminated by ' ' collection items terminated by '#' select * from student;
将查询的结果导出到HDFS上(没有local):insert overwrite directory '/export/servers/exporthive' row format delimited fields terminated by ' ' collection items terminated by '#' select * from score;
Hadoop命令导出到本地:dfs -get /export/servers/exporthive/000000_0 /export/servers/exporthive/local.txt;hive shell 命令导出
基本语法:(hive -f/-e 执行语句或者脚本 > file)hive -e "select * from myhive.score;" > /export/servers/exporthive/score.txt
hive -f export.sh > /export/servers/exporthive/score.txt
export导出到HDFS上:export table score to '/export/exporthive/score';Hive查询语句
GROUP BY 分组:select s_id ,avg(s_score) avgscore from score group by s_id having avgscore > 85; 对分组后的数据进行筛选,使用 having
join 连接:inner join 内连接;left join 左连接;right join 右链接;full join 全外链接。
order by 排序:ASC(ascend): 升序(默认) DESC(descend): 降序
sort by 局部排序:每个MapReduce内部进行排序,对全局结果集来说不是排序。
distribute by 分区排序:类似MR中partition,进行分区,结合sort by使用
Hive函数1. 聚合函数
指定列值的数目:count()
指定列值求和:sum()
指定列的最大值:max()
指定列的最小值:min()
指定列的平均值:avg()
非空集合总体变量函数:var_pop(col)
非空集合样本变量函数:var_samp (col)
总体标准偏离函数:stddev_pop(col)
分位数函数:percentile(BIGINT col, p)
中位数函数:percentile(BIGINT col, 0.5)
2. 关系运算
A LIKE B:LIKE比较,如果字符串A符合表达式B 的正则语法,则为TRUE
A RLIKE B:JAVA的LIKE操作,如果字符串A符合JAVA正则表达式B的正则语法,则为TRUE
A REGEXP B:功能与RLIKE相同
3. 数学运算
支持所有数值类型:加(+)、减(-)、乘(*)、除(/)、取余(%)、位与(&)、位或(|)、位异或(^)、位取反(~)
4. 逻辑运算
支持:逻辑与(and)、逻辑或(or)、逻辑非(not)
5. 数值运算
取整函数:round(double a)
指定精度取整函数:round(double a, int d)
向下取整函数:floor(double a)
向上取整函数:ceil(double a)
取随机数函数:rand(),rand(int seed)
自然指数函数:exp(double a)
以10为底对数函数:log10(double a)
以2为底对数函数:log2()
对数函数:log()
幂运算函数:pow(double a, double p)
开平方函数:sqrt(double a)
二进制函数:bin(BIGINT a)
十六进制函数:hex()
绝对值函数:abs()
正取余函数:pmod()
6. 条件函数
if
case when
coalesce(c1,c2,c3)
nvl(c1,c2)
7. 日期函数
获得当前时区的UNIX时间戳: unix_timestamp()
时间戳转日期函数:from_unixtime()
日期转时间戳:unix_timestamp(string date)
日期时间转日期函数:to_date(string timestamp)
日期转年函数:year(string date)
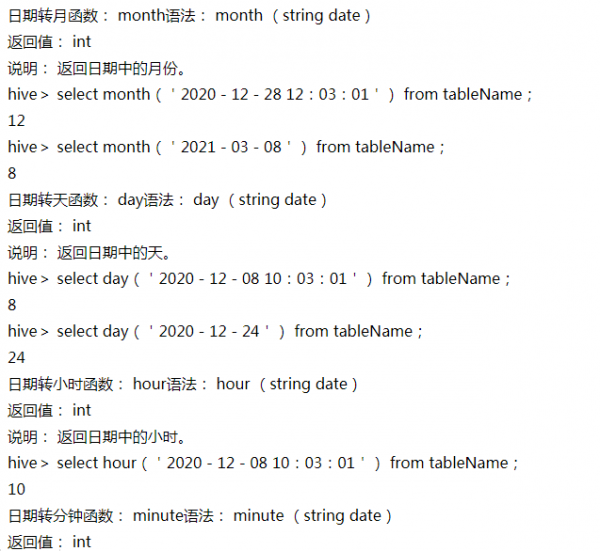
日期转月函数:month (string date)
日期转天函数: day (string date)
日期转小时函数: hour (string date)
日期转分钟函数:minute (string date)
日期转秒函数: second (string date)
日期转周函数: weekofyear (string date)
日期比较函数: datediff(string enddate, string startdate)
日期增加函数: date_add(string startdate, int days)
日期减少函数:date_sub (string startdate, int days)
8. 字符串函数
字符串长度函数:length(string A)
字符串反转函数:reverse(string A)
字符串连接函数: concat(string A, string B…)
带分隔符字符串连接函数:concat_ws(string SEP, string A, string B…)
字符串截取函数: substr(string A, int start, int len)
字符串转大写函数: upper(string A)
字符串转小写函数:lower(string A)
去空格函数:trim(string A)
左边去空格函数:ltrim(string A)
右边去空格函数:rtrim(string A)
正则表达式替换函数:regexp_replace(string A, string B, string C)
正则表达式解析函数: regexp_extract(string subject, string pattern, int index)
URL解析函数:parse_url(string urlString, string partToExtract [, string keyToExtract])返回值: string
json解析函数:get_json_object(string json_string, string path)
空格字符串函数:space(int n)
重复字符串函数:repeat(string str, int n)
首字符ascii函数:ascii(string str)
左补足函数:lpad(string str, int len, string pad)
右补足函数:rpad(string str, int len, string pad)
分割字符串函数: split(string str, string pat)
集合查找函数: find_in_set(string str, string strList)
9. 窗口函数
分组求和函数:sum(pv) over(partition by cookieid order by createtime) 有坑,加不加 order by 差别很大,具体详情在下面第二部分。
分组内排序,从1开始顺序排:ROW_NUMBER() 如:1234567
分组内排序,排名相等会在名次中留下空位:RANK() 如:1233567
分组内排序,排名相等不会在名次中留下空位:DENSE_RANK() 如:1233456
有序的数据集合平均分配到指定的数量(num)个桶中:NTILE()
统计窗口内往上第n行值:LAG(col,n,DEFAULT)
统计窗口内往下第n行值:LEAD(col,n,DEFAULT)
分组内排序后,截止到当前行,第一个值:FIRST_VALUE(col)
分组内排序后,截止到当前行,最后一个值: LAST_VALUE(col)
小于等于当前值的行数/分组内总行数:CUME_DIST()
以下函数建议看第二部分详细理解下,此处仅简写,!
将多个group by 逻辑写在一个sql语句中: GROUPING SETS
根据GROUP BY的维度的所有组合进行聚合:CUBE
CUBE的子集,以最左侧的维度为主,从该维度进行层级聚合:ROLLUP
第二部分1. 对数据库的操作创建数据库:create database if not exists myhive;
说明:hive的表存放位置模式是由hive-site.xml当中的一个属性指定的 :hive.metastore.warehouse.dir
创建数据库并指定hdfs存储位置 :
create database myhive2 location '/myhive2';
修改数据库:alter database myhive2 set dbproperties('createtime'='20210329');
说明:可以使用alter database 命令来修改数据库的一些属性。但是数据库的元数据信息是不可更改的,包括数据库的名称以及数据库所在的位置
查看数据库详细信息查看数据库基本信息
hive (myhive)> desc database myhive2;
查看数据库更多详细信息
hive (myhive)> desc database extended myhive2;
删除数据库删除一个空数据库,如果数据库下面有数据表,那么就会报错
drop database myhive2;
强制删除数据库,包含数据库下面的表一起删除
drop database myhive cascade;





注意:
如果使用 group by 分组,则 select 后面只能写分组的字段或者聚合函数
where和having区别:
1 having是在 group by 分完组之后再对数据进行筛选,所以having 要筛选的字段只能是分组字段或者聚合函数
2 where 是从数据表中的字段直接进行的筛选的,所以不能跟在gruopby后面,也不能使用聚合函数
join 连接INNER JOIN 内连接:只有进行连接的两个表中都存在与连接条件相匹配的数据才会被保留下来
select * from techer t [inner] join course c on t.t_id = c.t_id; -- inner 可省略
LEFT OUTER JOIN 左外连接:左边所有数据会被返回,右边符合条件的被返回
select * from techer t left join course c on t.t_id = c.t_id; -- outer可省略
RIGHT OUTER JOIN 右外连接:右边所有数据会被返回,左边符合条件的被返回、
select * from techer t right join course c on t.t_id = c.t_id;
FULL OUTER JOIN 满外(全外)连接: 将会返回所有表中符合条件的所有记录。如果任一表的指定字段没有符合条件的值的话,那
就使用NULL值替代。
SELECT * FROM techer t FULL JOIN course c ON t.t_id = c.t_id ;
注:1. hive2版本已经支持不等值连接,就是 join on条件后面可以使用大于小于符号了;并且也支持 join on 条件后跟or (早前版本 on 后只支持 = 和 and,不支持 > < 和 or)
2.如hive执行引擎使用MapReduce,一个join就会启动一个job,一条sql语句中如有多个join,则会启动多个job
注意:表之间用逗号(,)连接和 inner join 是一样的
select * from table_a,table_b where table_a.id=table_b.id;
它们的执行效率没有区别,只是书写方式不同,用逗号是sql 89标准,join 是sql 92标准。用逗号连接后面过滤条件用 where ,用 join 连接后面过滤条件是 on。
order by 排序全局排序,只会有一个reduce
ASC(ascend): 升序(默认) DESC(descend): 降序
SELECT * FROM student s LEFT JOIN score sco ON s.s_id = sco.s_id ORDER BY sco.s_score DESC;
注意:order by 是全局排序,所以最后只有一个reduce,也就是在一个节点执行,如果数据量太大,就会耗费较长时间
sort by 局部排序每个MapReduce内部进行排序,对全局结果集来说不是排序。
设置reduce个数
set mapreduce.job.reduces=3;
查看设置reduce个数
set mapreduce.job.reduces;
查询成绩按照成绩降序排列
select * from score sort by s_score;
将查询结果导入到文件中(按照成绩降序排列)
insert overwrite local directory '/export/servers/hivedatas/sort' select * from score sort by s_score;
distribute by 分区排序distribute by:类似MR中partition,进行分区,结合sort by使用
设置reduce的个数,将我们对应的s_id划分到对应的reduce当中去
set mapreduce.job.reduces=7;
通过distribute by 进行数据的分区
* from score distribute by s_id sort by s_score;
注意:Hive要求 distribute by 语句要写在 sort by 语句之前
cluster by当distribute by和sort by字段相同时,可以使用cluster by方式.
cluster by除了具有distribute by的功能外还兼具sort by的功能。但是排序只能是正序排序,不能指定排序规则为ASC或者DESC。
以下两种写法等价
select * from score cluster by s_id;
select * from score distribute by s_id sort by s_id;
Hive函数聚合函数hive支持 count(),max(),min(),sum(),avg() 等常用的聚合函数
注意:
聚合操作时要注意null值
count(*) 包含null值,统计所有行数
count(id) 不包含null值
min 求最小值是不包含null,除非所有值都是null
avg 求平均值也是不包含null
非空集合总体变量函数: var_pop语法: var_pop(col)
返回值: double
说明: 统计结果集中col非空集合的总体变量(忽略null)
非空集合样本变量函数: var_samp语法: var_samp (col)
返回值: double
说明: 统计结果集中col非空集合的样本变量(忽略null)
总体标准偏离函数: stddev_pop语法: stddev_pop(col)
返回值: double
说明: 该函数计算总体标准偏离,并返回总体变量的平方根,其返回值与VAR_POP函数的平方根相同
中位数函数: percentile语法: percentile(BIGINT col, p)
返回值: double
说明: 求准确的第pth个百分位数,p必须介于0和1之间,但是col字段目前只支持整数,不支持浮点数类型
关系运算支持:等值(=)、不等值(!= 或 <>)、小于(<)、小于等于(<=)、大于(>)、大于等于(>=)
空值判断(is null)、非空判断(is not null)
LIKE比较: LIKE语法: A LIKE B
操作类型: strings
描述: 如果字符串A或者字符串B为NULL,则返回NULL;如果字符串A符合表达式B 的正则语法,则为TRUE;否则为FALSE。B中字符”_”表示任意单个字符,而字符”%”表示任意数量的字符。
JAVA的LIKE操作: RLIKE语法: A RLIKE B
操作类型: strings
描述: 如果字符串A或者字符串B为NULL,则返回NULL;如果字符串A符合JAVA正则表达式B的正则语法,则为TRUE;否则为FALSE。
REGEXP操作: REGEXP语法: A REGEXP B
操作类型: strings
描述: 功能与RLIKE相同
示例:select 1 from tableName where 'footbar' REGEXP '^f.*r$';
结果:1
数学运算支持所有数值类型:加(+)、减(-)、乘(*)、除(/)、取余(%)、位与(&)、位或(|)、位异或(^)、位取反(~)
逻辑运算支持:逻辑与(and)、逻辑或(or)、逻辑非(not)
数值运算取整函数: round语法: round(double a)
返回值: BIGINT
说明: 返回double类型的整数值部分 (遵循四舍五入)
示例:select round(3.1415926) from tableName;
结果:3
指定精度取整函数: round语法: round(double a, int d)
返回值: DOUBLE
说明: 返回指定精度d的double类型
hive> select round(3.1415926,4) from tableName;
3.1416
向下取整函数: floor语法: floor(double a)
返回值: BIGINT
说明: 返回等于或者小于该double变量的最大的整数
hive> select floor(3.641) from tableName;
3
向上取整函数: ceil语法: ceil(double a)
返回值: BIGINT
说明: 返回等于或者大于该double变量的最小的整数
hive> select ceil(3.1415926) from tableName;
4
取随机数函数: rand语法: rand(),rand(int seed)
返回值: double
说明: 返回一个0到1范围内的随机数。如果指定种子seed,则会等到一个稳定的随机数序列
hive> select rand() from tableName; -- 每次执行此语句得到的结果都不同
0.5577432776034763
hive> select rand(100) ; -- 只要指定种子,每次执行此语句得到的结果一样的
0.7220096548596434
自然指数函数: exp语法: exp(double a)
返回值: double
说明: 返回自然对数e的a次方
hive> select exp(2) ;
7.38905609893065
以10为底对数函数: log10语法: log10(double a)
返回值: double
说明: 返回以10为底的a的对数
hive> select log10(100) ;
2.0
此外还有:以2为底对数函数: log2()、对数函数: log()
幂运算函数: pow语法: pow(double a, double p)
返回值: double
说明: 返回a的p次幂
hive> select pow(2,4) ;
16.0
开平方函数: sqrt语法: sqrt(double a)
返回值: double
说明: 返回a的平方根
hive> select sqrt(16) ;
4.0
二进制函数: bin语法: bin(BIGINT a)
返回值: string
说明: 返回a的二进制代码表示
hive> select bin(7) ;
111


















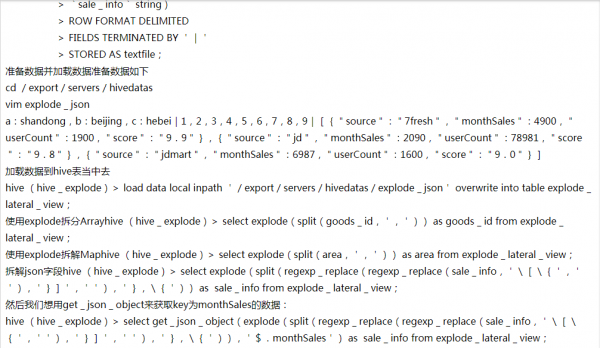

hive (hive_explode)> select get_json_object(concat('{',sale_info_1,'}'),'$.source') as source,get_json_object(concat('{',sale_info_1,'}'),'$.monthSales') as monthSales,get_json_object(concat('{',sale_info_1,'}'),'$.userCount') as monthSales,get_json_object(concat('{',sale_info_1,'}'),'$.score') as monthSales from explode_lateral_view LATERAL VIEW explode(split(regexp_replace(regexp_replace(sale_info,'\[\{',''),'}]',''),'},\{'))sale_info as sale_info_1;
总结:
Lateral View通常和UDTF一起出现,为了解决UDTF不允许在select字段的问题。Multiple Lateral View可以实现类似笛卡尔乘积。Outer关键字可以把不输出的UDTF的空结果,输出成NULL,防止丢失数据。
行转列
相关参数说明:
CONCAT(string A/col, string B/col…):返回输入字符串连接后的结果,支持任意个输入字符串;
CONCAT_WS(separator, str1, str2,...):它是一个特殊形式的 CONCAT()。第一个参数剩余参数间的分隔符。分隔符可以是与剩余参数一样的字符串。如果分隔符是 NULL,返回值也将为 NULL。这个函数会跳过分隔符参数后的任何 NULL 和空字符串。分隔符将被加到被连接的字符串之间;
COLLECT_SET(col):函数只接受基本数据类型,它的主要作用是将某字段的值进行去重汇总,产生array类型字段。
数据准备:
nameconstellationblood_type孙悟空白羊座A老王射手座A宋宋白羊座B猪八戒白羊座A凤姐射手座A
需求: 把星座和血型一样的人归类到一起。结果如下:
射手座,A 老王|凤姐
白羊座,A 孙悟空|猪八戒
白羊座,B 宋宋
实现步骤:
创建本地constellation.txt,导入数据node03服务器执行以下命令创建文件,注意数据使用 进行分割
cd /export/servers/hivedatas
vim constellation.txt
数据如下:
孙悟空 白羊座 A
老王 射手座 A
宋宋 白羊座 B
猪八戒 白羊座 A
凤姐 射手座 A
创建hive表并导入数据创建hive表并加载数据
hive (hive_explode)> create table person_info(
name string,
constellation string,
blood_type string)
row format delimited fields terminated by " ";
加载数据
hive (hive_explode)> load data local inpath '/export/servers/hivedatas/constellation.txt' into table person_info;
按需求查询数据hive (hive_explode)> select
t1.base,
concat_ws('|', collect_set(t1.name)) name
from
(select
name,
concat(constellation, "," , blood_type) base
from
person_info) t1
group by
t1.base;
列转行
所需函数:
EXPLODE(col):将hive一列中复杂的array或者map结构拆分成多行。
LATERAL VIEW
用法:LATERAL VIEW udtf(expression) tableAlias AS columnAlias
解释:用于和split, explode等UDTF一起使用,它能够将一列数据拆成多行数据,在此基础上可以对拆分后的数据进行聚合。
数据准备:
cd /export/servers/hivedatas
vim movie.txt
文件内容如下: 数据字段之间使用 进行分割
《疑犯追踪》 悬疑,动作,科幻,剧情
《Lie to me》 悬疑,警匪,动作,心理,剧情
《战狼2》 战争,动作,灾难
需求: 将电影分类中的数组数据展开。结果如下:
《疑犯追踪》 悬疑
《疑犯追踪》 动作
《疑犯追踪》 科幻
《疑犯追踪》 剧情
《Lie to me》 悬疑
《Lie to me》 警匪
《Lie to me》 动作
《Lie to me》 心理
《Lie to me》 剧情
《战狼2》 战争
《战狼2》 动作
《战狼2》 灾难
实现步骤:
创建hive表create table movie_info(
movie string,
category array<string>)
row format delimited fields terminated by " "
collection items terminated by ",";
加载数据load data local inpath "/export/servers/hivedatas/movie.txt" into table movie_info;
按需求查询数据select
movie,
category_name
from
movie_info lateral view explode(category) table_tmp as category_name;
reflect函数
reflect函数可以支持在sql中调用java中的自带函数,秒杀一切udf函数。
需求1: 使用java.lang.Math当中的Max求两列中最大值
实现步骤:
创建hive表create table test_udf(col1 int,col2 int) row format delimited fields terminated by ',';
准备数据并加载数据cd /export/servers/hivedatas
vim test_udf
文件内容如下:
1,2
4,3
6,4
7,5
5,6
加载数据hive (hive_explode)> load data local inpath '/export/servers/hivedatas/test_udf' overwrite into table test_udf;
使用java.lang.Math当中的Max求两列当中的最大值hive (hive_explode)> select reflect("java.lang.Math","max",col1,col2) from test_udf;
需求2: 文件中不同的记录来执行不同的java的内置函数
实现步骤:
创建hive表hive (hive_explode)> create table test_udf2(class_name string,method_name string,col1 int , col2 int) row format delimited fields terminated by ',';
准备数据cd /export/servers/hivedatas
vim test_udf2
文件内容如下:
java.lang.Math,min,1,2
java.lang.Math,max,2,3
加载数据hive (hive_explode)> load data local inpath '/export/servers/hivedatas/test_udf2' overwrite into table test_udf2;
执行查询hive (hive_explode)> select reflect(class_name,method_name,col1,col2) from test_udf2;
需求3: 判断是否为数字
实现方式:
使用apache commons中的函数,commons下的jar已经包含在hadoop的classpath中,所以可以直接使用。
select reflect("org.apache.commons.lang.math.NumberUtils","isNumber","123")
Hive 窗口函数
窗口函数最重要的关键字是 partition by 和 order by
具体语法如下:XXX over (partition by xxx order by xxx)
特别注意:over()里面的 partition by 和 order by 都不是必选的,over()里面可以只有partition by,也可以只有order by,也可以两个都没有,大家需根据需求灵活运用。
窗口函数我划分了几个大类,我们一类一类的讲解。
1. SUM、AVG、MIN、MAX
讲解这几个窗口函数前,先创建一个表,以实际例子讲解大家更容易理解。
首先创建用户访问页面表:user_pv
create table user_pv(
cookieid string, -- 用户登录的cookie,即用户标识
createtime string, -- 日期
pv int -- 页面访问量
);
给上面这个表加上如下数据:
cookie1,2021-05-10,1
cookie1,2021-05-11,5
cookie1,2021-05-12,7
cookie1,2021-05-13,3
cookie1,2021-05-14,2
cookie1,2021-05-15,4
cookie1,2021-05-16,4
SUM()使用
执行如下查询语句:
select cookieid,createtime,pv,
sum(pv) over(partition by cookieid order by createtime) as pv1
from user_pv;
结果如下:(因命令行原因,下图字段名和值是错位的,请注意辨别!)
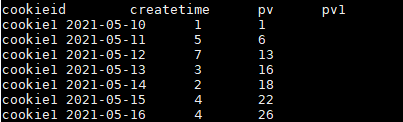
执行如下查询语句:
select cookieid,createtime,pv,
sum(pv) over(partition by cookieid ) as pv1
from user_pv;
结果如下:
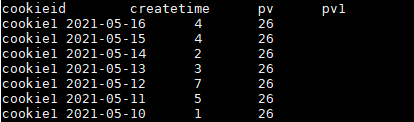
第一条SQL的over()里面加 order by ,第二条SQL没加order by ,结果差别很大
所以要注意了:
over()里面加 order by 表示:分组内从起点到当前行的pv累积,如,11号的pv1=10号的pv+11号的pv, 12号=10号+11号+12号;
over()里面不加 order by 表示:将分组内所有值累加。
AVG,MIN,MAX,和SUM用法一样,这里就不展开讲了,但是要注意 AVG,MIN,MAX 的over()里面加不加 order by 也和SUM一样,如 AVG 求平均值,如果加上 order by,表示分组内从起点到当前行的平局值,不是全部的平局值。MIN,MAX 同理。
2. ROW_NUMBER、RANK、DENSE_RANK、NTILE
还是用上述的用户登录日志表:user_pv,里面的数据换成如下所示:
cookie1,2021-05-10,1
cookie1,2021-05-11,5
cookie1,2021-05-12,7
cookie1,2021-05-13,3
cookie1,2021-05-14,2
cookie1,2021-05-15,4
cookie1,2021-05-16,4
cookie2,2021-05-10,2
cookie2,2021-05-11,3
cookie2,2021-05-12,5
cookie2,2021-05-13,6
cookie2,2021-05-14,3
cookie2,2021-05-15,9
cookie2,2021-05-16,7
ROW_NUMBER()使用:
ROW_NUMBER()从1开始,按照顺序,生成分组内记录的序列。
SELECT
cookieid,
createtime,
pv,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY cookieid ORDER BY pv desc) AS rn
FROM user_pv;
结果如下:

RANK 和 DENSE_RANK 使用:
RANK() 生成数据项在分组中的排名,排名相等会在名次中留下空位。
DENSE_RANK()生成数据项在分组中的排名,排名相等会在名次中不会留下空位。
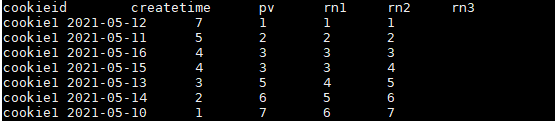
SELECT
cookieid,
createtime,
pv,
RANK() OVER(PARTITION BY cookieid ORDER BY pv desc) AS rn1,
DENSE_RANK() OVER(PARTITION BY cookieid ORDER BY pv desc) AS rn2,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY cookieid ORDER BY pv DESC) AS rn3
FROM user_pv
WHERE cookieid = 'cookie1';
结果如下:
NTILE的使用:
有时会有这样的需求:如果数据排序后分为三部分,业务人员只关心其中的一部分,如何将这中间的三分之一数据拿出来呢?NTILE函数即可以满足。
ntile可以看成是:把有序的数据集合平均分配到指定的数量(num)个桶中, 将桶号分配给每一行。如果不能平均分配,则优先分配较小编号的桶,并且各个桶中能放的行数最多相差1。
然后可以根据桶号,选取前或后 n分之几的数据。数据会完整展示出来,只是给相应的数据打标签;具体要取几分之几的数据,需要再嵌套一层根据标签取出。
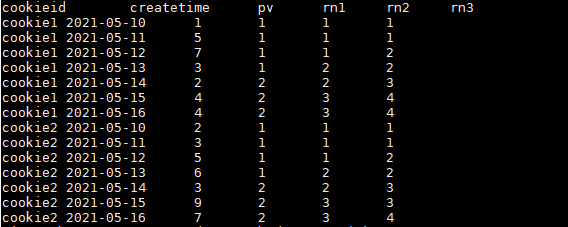
SELECT
cookieid,
createtime,
pv,
NTILE(2) OVER(PARTITION BY cookieid ORDER BY createtime) AS rn1,
NTILE(3) OVER(PARTITION BY cookieid ORDER BY createtime) AS rn2,
NTILE(4) OVER(ORDER BY createtime) AS rn3
FROM user_pv
ORDER BY cookieid,createtime;
结果如下:
3. LAG、LEAD、FIRST_VALUE、LAST_VALUE
讲解这几个窗口函数时还是以实例讲解,首先创建用户访问页面表:user_url
CREATE TABLE user_url (
cookieid string,
createtime string, --页面访问时间
url string --被访问页面
);
表中加入如下数据:
cookie1,2021-06-10 10:00:02,url2
cookie1,2021-06-10 10:00:00,url1
cookie1,2021-06-10 10:03:04,1url3
cookie1,2021-06-10 10:50:05,url6
cookie1,2021-06-10 11:00:00,url7
cookie1,2021-06-10 10:10:00,url4
cookie1,2021-06-10 10:50:01,url5
cookie2,2021-06-10 10:00:02,url22
cookie2,2021-06-10 10:00:00,url11
cookie2,2021-06-10 10:03:04,1url33
cookie2,2021-06-10 10:50:05,url66
cookie2,2021-06-10 11:00:00,url77
cookie2,2021-06-10 10:10:00,url44
cookie2,2021-06-10 10:50:01,url55
LAG的使用:
LAG(col,n,DEFAULT) 用于统计窗口内往上第n行值。
第一个参数为列名,第二个参数为往上第n行(可选,默认为1),第三个参数为默认值(当往上第n行为NULL时候,取默认值,如不指定,则为NULL)
SELECT cookieid,
createtime,
url,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY cookieid ORDER BY createtime) AS rn,
LAG(createtime,1,'1970-01-01 00:00:00') OVER(PARTITION BY cookieid ORDER BY createtime) AS last_1
time,
LAG(createtime,2) OVER(PARTITION BY cookieid ORDER BY createtime) AS last_2_time
FROM user_url;
结果如下:
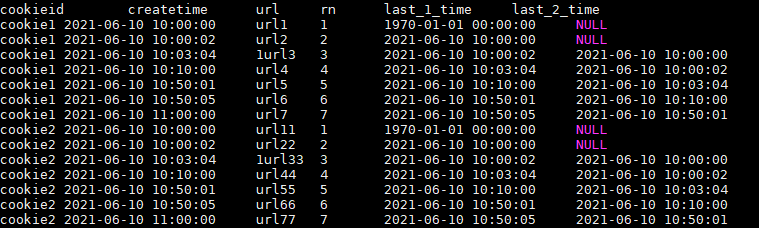
解释:
last_1_time: 指定了往上第1行的值,default为'1970-01-01 00:00:00'
cookie1第一行,往上1行为NULL,因此取默认值 1970-01-01 00:00:00
cookie1第三行,往上1行值为第二行值,2021-06-10 10:00:02
cookie1第六行,往上1行值为第五行值,2021-06-10 10:50:01
last_2_time: 指定了往上第2行的值,为指定默认值
cookie1第一行,往上2行为NULL
cookie1第二行,往上2行为NULL
cookie1第四行,往上2行为第二行值,2021-06-10 10:00:02
cookie1第七行,往上2行为第五行值,2021-06-10 10:50:01
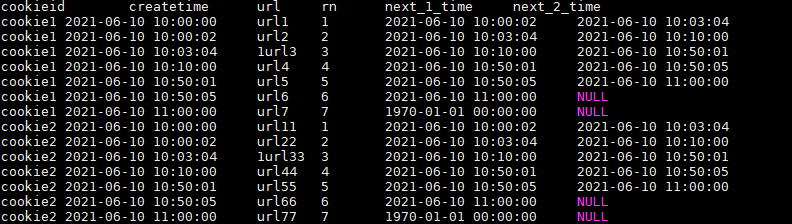
LEAD的使用:
与LAG相反
LEAD(col,n,DEFAULT) 用于统计窗口内往下第n行值。
第一个参数为列名,第二个参数为往下第n行(可选,默认为1),第三个参数为默认值(当往下第n行为NULL时候,取默认值,如不指定,则为NULL)
SELECT cookieid,
createtime,
url,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY cookieid ORDER BY createtime) AS rn,
LEAD(createtime,1,'1970-01-01 00:00:00') OVER(PARTITION BY cookieid ORDER BY createtime) AS next__time,
LEAD(createtime,2) OVER(PARTITION BY cookieid ORDER BY createtime) AS next_2_time
FROM user_url;
结果如下:
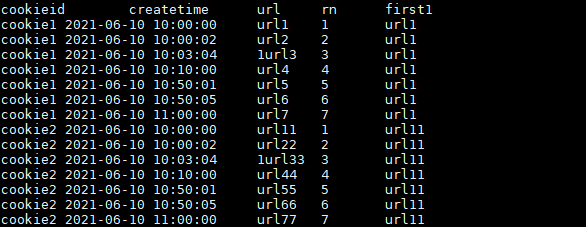
FIRST_VALUE的使用:
取分组内排序后,截止到当前行,第一个值。
SELECT cookieid,
createtime,
url,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY cookieid ORDER BY createtime) AS rn,
FIRST_VALUE(url) OVER(PARTITION BY cookieid ORDER BY createtime) AS first1
FROM user_url;
结果如下:
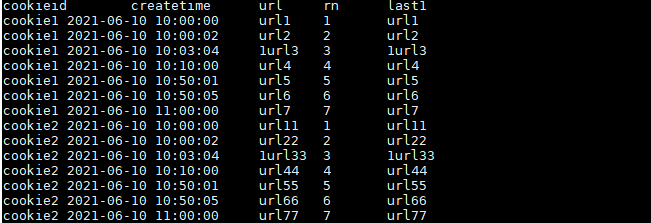
LAST_VALUE的使用:
取分组内排序后,截止到当前行,最后一个值。
SELECT cookieid,
createtime,
url,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY cookieid ORDER BY createtime) AS rn,
LAST_VALUE(url) OVER(PARTITION BY cookieid ORDER BY createtime) AS last1
FROM user_url;
结果如下:
如果想要取分组内排序后最后一个值,则需要变通一下:
SELECT cookieid,
createtime,
url,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY cookieid ORDER BY createtime) AS rn,
LAST_VALUE(url) OVER(PARTITION BY cookieid ORDER BY createtime) AS last1,
FIRST_VALUE(url) OVER(PARTITION BY cookieid ORDER BY createtime DESC) AS last2
FROM user_url
ORDER BY cookieid,createtime;
注意上述SQL,使用的是 FIRST_VALUE 的倒序取出分组内排序最后一个值!
结果如下:
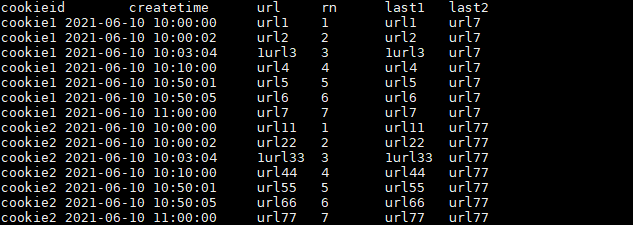
此处要特别注意order by
如果不指定ORDER BY,则进行排序混乱,会出现错误的结果
SELECT cookieid,
createtime,
url,
FIRST_VALUE(url) OVER(PARTITION BY cookieid) AS first2
FROM user_url;
结果如下:
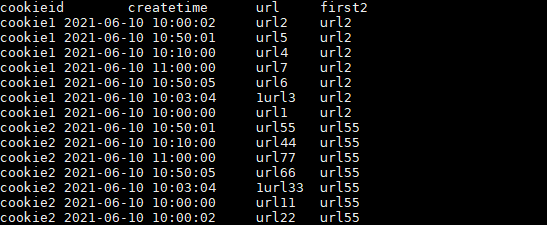
上述 url2 和 url55 的createtime即不属于最靠前的时间也不属于最靠后的时间,所以结果是混乱的。
4. CUME_DIST
先创建一张员工薪水表:staff_salary
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE staff_salary (
dept string,
userid string,
sal int
);
表中加入如下数据:
d1,user1,1000
d1,user2,2000
d1,user3,3000
d2,user4,4000
d2,user5,5000
CUME_DIST的使用:
此函数的结果和order by的排序顺序有关系。
CUME_DIST:小于等于当前值的行数/分组内总行数。order默认顺序:正序
比如,统计小于等于当前薪水的人数,所占总人数的比例。
SELECT
dept,
userid,
sal,
CUME_DIST() OVER(ORDER BY sal) AS rn1,
CUME_DIST() OVER(PARTITION BY dept ORDER BY sal) AS rn2
FROM staff_salary;
结果如下:
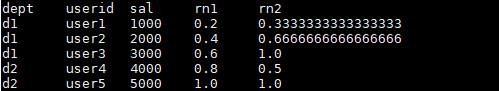
解释:
rn1: 没有partition,所有数据均为1组,总行数为5,
第一行:小于等于1000的行数为1,因此,1/5=0.2
第三行:小于等于3000的行数为3,因此,3/5=0.6
rn2: 按照部门分组,dpet=d1的行数为3
第二行:小于等于2000的行数为2,因此,2/3=0.6666666666666666
5. GROUPING SETS、GROUPING__ID、CUBE、ROLLUP
这几个分析函数通常用于OLAP中,不能累加,而且需要根据不同维度上钻和下钻的指标统计,比如,分小时、天、月的UV数。
还是先创建一个用户访问表:user_date
CREATE TABLE user_date (
month STRING,
day STRING,
cookieid STRING
);
表中加入如下数据:
2021-03,2021-03-10,cookie1
2021-03,2021-03-10,cookie5
2021-03,2021-03-12,cookie7
2021-04,2021-04-12,cookie3
2021-04,2021-04-13,cookie2
2021-04,2021-04-13,cookie4
2021-04,2021-04-16,cookie4
2021-03,2021-03-10,cookie2
2021-03,2021-03-10,cookie3
2021-04,2021-04-12,cookie5
2021-04,2021-04-13,cookie6
2021-04,2021-04-15,cookie3
2021-04,2021-04-15,cookie2
2021-04,2021-04-16,cookie1
GROUPING SETS的使用:
grouping sets是一种将多个group by 逻辑写在一个sql语句中的便利写法。
等价于将不同维度的GROUP BY结果集进行UNION ALL。
SELECT
month,
day,
COUNT(DISTINCT cookieid) AS uv,
GROUPING__ID
FROM user_date
GROUP BY month,day
GROUPING SETS (month,day)
ORDER BY GROUPING__ID;
注:上述SQL中的GROUPING__ID,是个关键字,表示结果属于哪一个分组集合,根据grouping sets中的分组条件month,day,1是代表month,2是代表day。
结果如下:
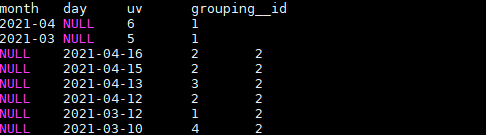
上述SQL等价于:
SELECT month,
NULL as day,
COUNT(DISTINCT cookieid) AS uv,
1 AS GROUPING__ID
FROM user_date
GROUP BY month
UNION ALL
SELECT NULL as month,
day,
COUNT(DISTINCT cookieid) AS uv,
2 AS GROUPING__ID
FROM user_date
GROUP BY day;
CUBE的使用:
根据GROUP BY的维度的所有组合进行聚合。
SELECT
month,
day,
COUNT(DISTINCT cookieid) AS uv,
GROUPING__ID
FROM user_date
GROUP BY month,day
WITH CUBE
ORDER BY GROUPING__ID;
结果如下:
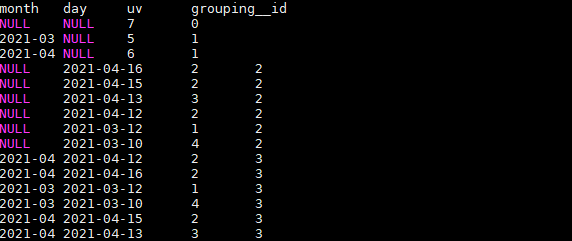
上述SQL等价于:
SELECT NULL,NULL,COUNT(DISTINCT cookieid) AS uv,0 AS GROUPING__ID FROM user_date
UNION ALL
SELECT month,NULL,COUNT(DISTINCT cookieid) AS uv,1 AS GROUPING__ID FROM user_date GROUP BY month
UNION ALL
SELECT NULL,day,COUNT(DISTINCT cookieid) AS uv,2 AS GROUPING__ID FROM user_date GROUP BY day
UNION ALL
SELECT month,day,COUNT(DISTINCT cookieid) AS uv,3 AS GROUPING__ID FROM user_date GROUP BY month,day;
ROLLUP的使用:
是CUBE的子集,以最左侧的维度为主,从该维度进行层级聚合。
比如,以month维度进行层级聚合:
SELECT
month,
day,
COUNT(DISTINCT cookieid) AS uv,
GROUPING__ID
FROM user_date
GROUP BY month,day
WITH ROLLUP
ORDER BY GROUPING__ID;
结果如下:
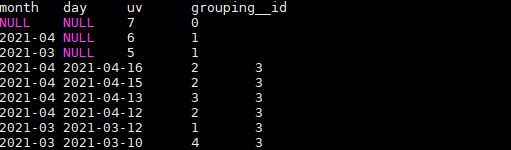
把month和day调换顺序,则以day维度进行层级聚合:
SELECT
day,
month,
COUNT(DISTINCT cookieid) AS uv,
GROUPING__ID
FROM user_date
GROUP BY day,month
WITH ROLLUP
ORDER BY GROUPING__ID;
结果如下:
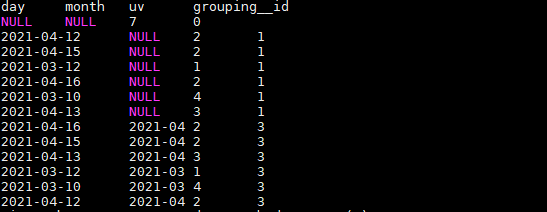
这里,根据日和月进行聚合,和根据日聚合结果一样,因为有父子关系,如果是其他维度组合的话,就会不一样。

